Introduction
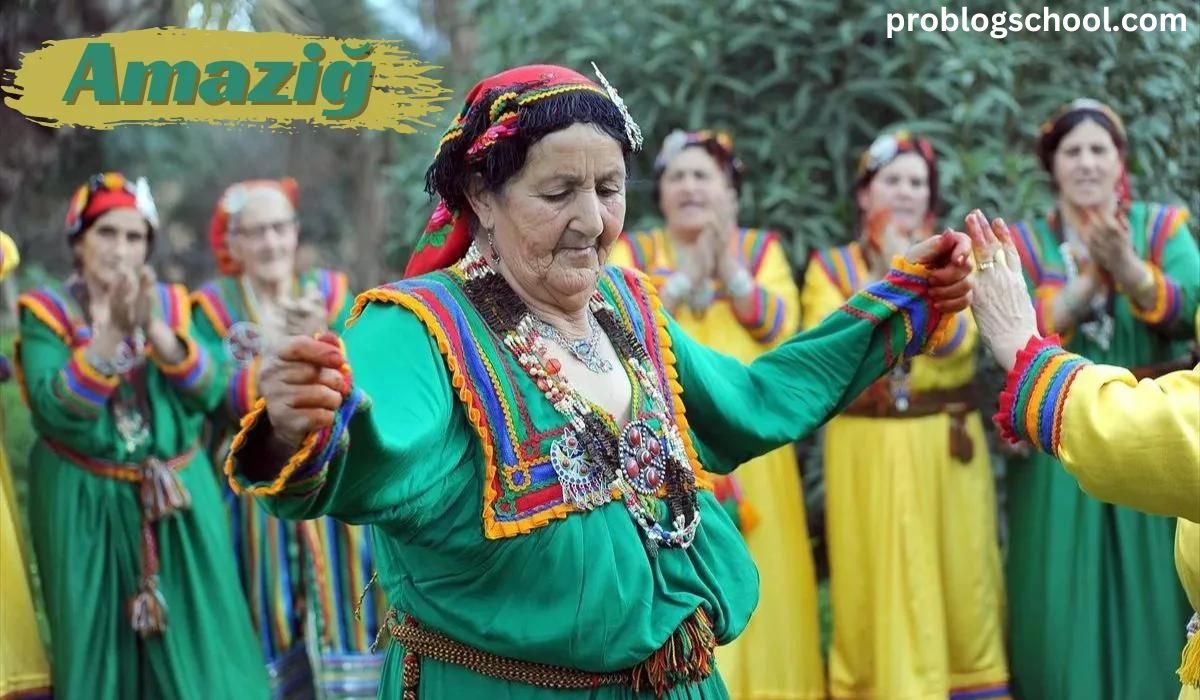
The history of the Amaziğ people, also referred to as Berbers, is extensive and dates back thousands of years. Despite several rounds of conquest and invasion, these native people of North Africa have managed to preserve their unique cultural identity. The narrative of the Amaziğ is one of perseverance and unwavering pride, spanning from their prehistoric beginnings to their contemporary challenges and accomplishments. This article explores the historical background, linguistic legacy, customs, and contemporary status of the Amaziğ people.
Part 1: Ancient Origins and Historical Context
Pre-Roman Amaziğ
The roots of the Amaziğ people extend deep into antiquity, with evidence of early settlements scattered across North Africa. Archaeological findings have revealed that these communities thrived in areas that are now modern-day Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and parts of the Sahara Desert. The Amazig played a crucial role in the development of ancient North African civilizations, including the Carthaginian and Numidian states.
These early Amazig communities were adept at adapting to their environment, developing agricultural practices suited to the varied landscapes they inhabited. Their ability to harness the resources of both coastal and desert regions allowed them to sustain flourishing societies long before the arrival of external powers.
Roman Conquest and Influence
The arrival of the Romans in North Africa marked a significant turning point in Amaziğ history. The Roman conquest brought about profound changes, as the Amaziğ were integrated into the vast Roman Empire. Roman rule introduced new technologies, administrative practices, and cultural influences that left a lasting impact on Amaziğ society.
However, the Amaziğ were not passive recipients of Roman culture. Instead, they actively engaged in a process of cultural exchange, blending Roman customs with their own traditions. This period also saw the emergence of prominent Amaziğ figures, such as the Numidian king Jugurtha, who played a key role in resisting Roman expansion.
Islamic Conquest and Adaptation
The Islamic conquest of North Africa in the 7th century CE brought another wave of transformation to the Amaziğ people. The spread of Islam was embraced by the Amaziğ, leading to significant changes in their religious and cultural practices. Islamic teachings became deeply integrated into Amaziğ society, influencing everything from their legal systems to their art and architecture.
Despite the widespread adoption of Islam, the Amaziğ maintained many of their pre-Islamic traditions, blending them with their new faith. Amaziğ scholars and intellectuals made significant contributions to the Islamic world, particularly in the fields of philosophy, science, and literature.
Part 2: Linguistic Heritage and Preservation
Amaziğ Languages
The Amaziğ people are known for their linguistic diversity, with several distinct languages spoken across the region. The most prominent of these languages include Tamazight, Kabyle, and Tachelhit. Each of these languages has its own unique characteristics, reflecting the rich cultural tapestry of the Amaziğ people.
Tamazight, for example, is spoken primarily in Morocco and is recognized as an official language alongside Arabic. Kabyle, on the other hand, is spoken in the Kabylie region of Algeria and has a strong literary tradition. The linguistic diversity of the Amaziğ is a testament to their deep-rooted cultural heritage, which has been passed down through generations.
Language Revitalization Efforts
In the modern era, the Amaziğ languages face numerous challenges, including the pressures of globalization and the dominance of other languages such as Arabic and French. However, there have been concerted efforts to preserve and revitalize these languages. Educational initiatives, cultural programs, and the use of technology have all played a role in ensuring that Amaziğ languages continue to thrive.
The introduction of Amaziğ languages into school curricula in countries like Morocco and Algeria is a significant step toward preserving these languages for future generations. Additionally, the rise of digital platforms has provided new opportunities for the promotion of Amaziğ languages, with social media and online content playing a crucial role in their revitalization.
Part 3: Traditional Customs and Practices
Amaziğ Society and Social Structure
The social structure of the Amaziğ people is deeply rooted in family, kinship, and community bonds. Amaziğ society is traditionally organized into tribes, with each tribe consisting of several extended families. These tribes are often led by a council of elders who play a crucial role in maintaining social order and resolving disputes.
Gender dynamics within Amaziğ society have traditionally been shaped by a division of labor, with men and women taking on complementary roles. While men have typically been responsible for tasks such as herding and farming, women have played a central role in managing household affairs and preserving cultural traditions.
Art, Music, and Literature
The Amaziğ people have a rich artistic heritage, with their creative expressions taking various forms, including painting, sculpture, pottery, and textile work. Traditional Amaziğ art is often characterized by intricate geometric patterns and vibrant colors, reflecting the natural beauty of their surroundings.
Music and dance are also integral to Amaziğ culture, with traditional instruments such as the guembri and bendir used to create rhythmic and melodic compositions. Amaziğ music often serves as a means of storytelling, with lyrics that recount historical events, celebrate communal values, and convey spiritual messages.
Oral literature has been a cornerstone of Amaziğ culture, with storytelling serving as a way to preserve historical narratives, moral lessons, and cultural knowledge. The rich oral traditions of the Amaziğ have been passed down through generations, ensuring that their cultural heritage remains alive and vibrant.
Festivals and Celebrations
The Amaziğ people celebrate a variety of festivals throughout the year, each with its own unique significance. One of the most important festivals is Yennayer, the Amaziğ New Year, which is celebrated in mid-January. This festival marks the beginning of the agricultural year and is a time for families to come together, share meals, and partake in traditional rituals.
Other significant celebrations include Imilchil Marriage Festival in Morocco, which is a celebration of love and union, and Awal, a festival dedicated to honoring ancestors. These festivals provide an opportunity for the Amaziğ people to reaffirm their cultural identity and pass on their traditions to younger generations.
Part 4: The Amaziğ in the Modern World
Challenges and Discrimination
Despite their rich cultural heritage, the Amaziğ people have faced numerous challenges throughout history, including marginalization and discrimination. In many North African countries, the Amaziğ have struggled to gain recognition for their cultural and linguistic rights. This has led to a sense of disenfranchisement among many Amaziğ communities, who feel that their contributions to national identity have been overlooked.
Contemporary challenges include the pressures of modernization, which have led to the erosion of traditional practices and languages. Additionally, political and social marginalization continues to be a significant issue, with many Amaziğ activists advocating for greater autonomy and cultural recognition.
Amaziğ Identity and Activism
In recent decades, there has been a resurgence of Amaziğ identity, with many individuals and organizations working to promote and preserve their cultural heritage. The Amaziğ identity movement has gained momentum, particularly in countries like Morocco and Algeria, where activists have successfully lobbied for the recognition of Amaziğ languages and the inclusion of Amaziğ culture in national narratives.
Amaziğ organizations, such as the World Amazigh Congress and various local cultural associations, have played a crucial role in advocating for the rights of the Amaziğ people. These organizations work to raise awareness about the challenges facing the Amaziğ and to promote their cultural and linguistic heritage on a global stage.
Amaziğ Culture in the Global Context
The Amaziğ people have made significant contributions to global culture, particularly in the fields of art, music, and literature. The global Amaziğ diaspora, which includes communities in Europe, North America, and beyond, has played a key role in promoting Amaziğ culture internationally. Through festivals, cultural events, and online platforms, the Amaziğ diaspora has helped to raise awareness about their rich heritage and to foster connections between Amaziğ communities around the world.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in Amaziğ culture from the global community, with many people drawn to their unique artistic expressions, traditional music, and rich history. This increased visibility has helped to combat stereotypes and misconceptions about the Amaziğ people, highlighting their contributions to global diversity and cultural exchange.
Conclusion
The history of the Amaziđ people is extensive and intricate, closely entwined with that of North Africa. The Amazič have proven to be remarkably resilient and have a strong dedication to maintaining their cultural identity, as seen by their challenges and accomplishments in current times, as well as their ancient beginnings. It is crucial to acknowledge and honor the achievements of indigenous peoples like the Amaziğ, especially as the globe grows increasingly linked.
We may appreciate the richness of human culture and the lasting strength of tradition more fully when we comprehend the rich legacy of the Amaziđ people. The Amaziď people continue to have a significant position in the worldwide cultural scene, whether it be through language revitalization initiatives, cultural festivals, or the promotion of their creative history.
FAQs
What is the historical significance of the Amaziğ people?
The Amaziğ people, also known as Berbers, are indigenous to North Africa and have a rich history that dates back thousands of years. They have played a significant role in shaping the region’s culture and history, influencing major civilizations like the Carthaginians and the Numidians.
What languages do the Amaziğ people speak?
The Amaziğ people speak a variety of languages, including Tamazight, Kabyle, and Tachelhit. These languages have distinct regional variations and are part of the Afroasiatic language family.
How have the Amaziğ preserved their cultural heritage?
The Amaziğ have preserved their cultural heritage through oral traditions, festivals, and the revitalization of their languages. Despite challenges, they continue to celebrate their identity through art, music, and traditional practices.
What are some important Amaziğ festivals?
One of the most important Amaziğ festivals is Yennayer, the Amaziğ New Year, celebrated in mid-January. Other significant festivals include the Imilchil Marriage Festival and Awal, which honors ancestors.
What challenges do the Amaziğ face today?
Today, the Amaziğ people face challenges such as cultural marginalization, language decline, and discrimination. However, there is a growing movement to preserve and promote their identity and rights.